DSA - Binary Search Recipe
When it comes to binary search, software engineers are like split in half. Its too basic, But some including me, always mess up with the index manipulation.
Binary search basically allow us to find a value in a sorted array in O(log n) time. The space complexity is O(1) and if its implemented using recursive call stack approach, the space complexity will be O(log n). The Binary has many uses beyond the basic use case of finding a value in sorted array.
Lets see how Binary Search Recipe makes easy to remember Binary Search Algorithm and solve related Problems.
Binary Search Recipe:
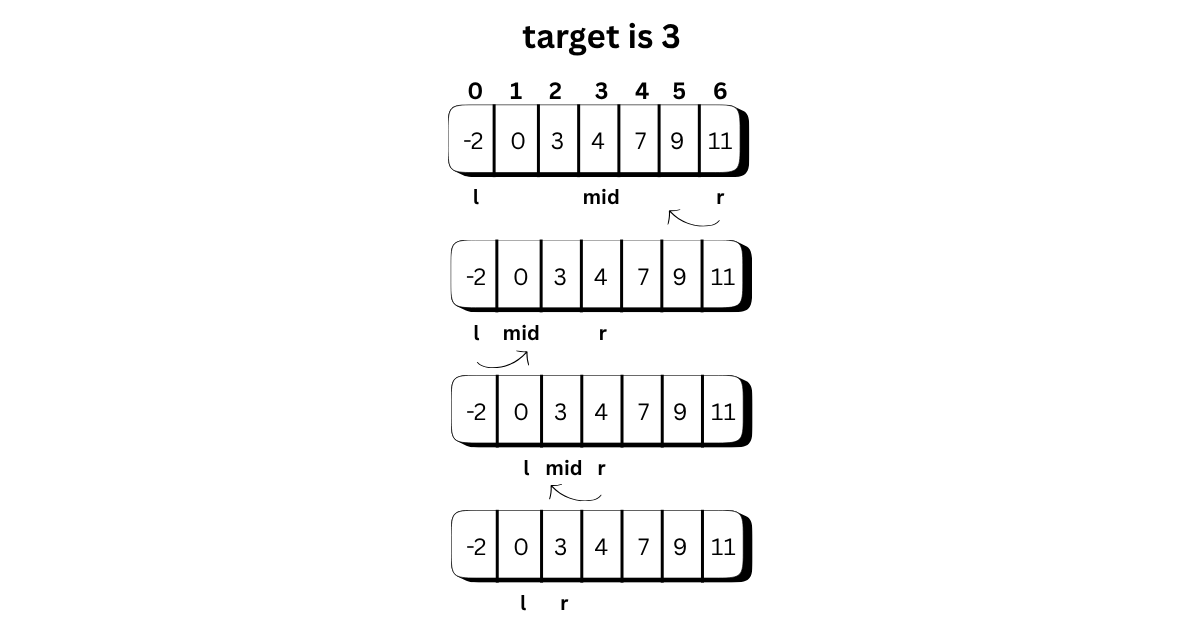
If array length is 0 return -1
Initialize l and r to the first and last indexes in the array
handle edge cases:
if target is less than first value or greater than last value in array return -1
if target is equal to first element in array return it
while l and r are not next to each other (r -l > 1)
mid = (l + r) / 2
if target is greater than mid value
l = mid
else
r = mid
if target is equal to right value return it
return -1
// Example of Implementation in Java
package binarySearch;
import java.util.*;
class SearchInSortedArray {
public static void main(String[] main) {
SearchInSortedArrayTests runTests = new SearchInSortedArrayTests();
runTests.runTests();
}
public int solve(int[] arr, int target) {
if (arr.length == 0) {
return -1;
}
int l = 0, r = arr.length - 1;
if (target <= arr[l] || target > arr[r]) {
if (target == arr[l]) {
return l;
}
return -1;
}
while (r - l > 1) {
int mid = (l + r) / 2;
if (target > arr[mid]) {
l = mid;
} else {
r = mid;
}
}
if (target == arr[r]) {
return r;
}
return -1;
}
}
class SearchInSortedArrayTests {
public void runTests() {
Object[][] tests = {
{new int[] {-2, 0, 3, 4, 7, 9, 11}, 3, 2},
{new int[] {-2, 0, 3, 4, 7, 9, 11}, 2, -1},
{new int[] {-2, 0, 3, 4, 7, 9, 11}, 9, 5},
// Edge case - empty array
{new int[] {}, 5, -1},
// Edge case - target at start
{new int[] {1, 2, 3}, 1, 0},
// Edge case - target at end
{new int[] {1, 2, 3}, 3, 2},
// Edge case - single element
{new int[] {5}, 5, 0},
// Edge case - not found
{new int[] {1, 3, 5}, 2, -1}
};
SearchInSortedArray solution = new SearchInSortedArray();
for (Object[] test : tests) {
int[] arr = (int[]) test[0];
int target = (int) test[1];
int want = (int) test[2];
int got = solution.solve(arr, target);
if (got != want) {
throw new RuntimeException(
String.format(
"\nsolve(%s, %d): got: %d, want: %d\n", Arrays.toString(arr), target, got, want));
} else {
System.out.print(".");
}
}
}
}