DSA - Binary Tree Traversals - DFS Vs BFS
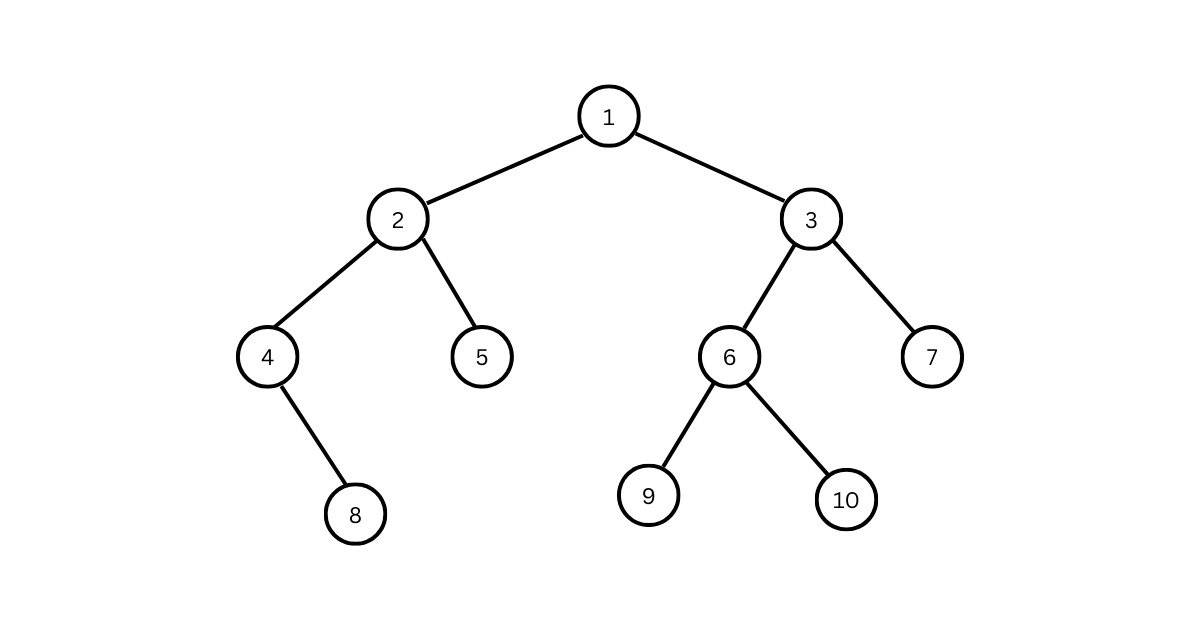
A binary tree is a recursive data structure where each node can have two children at most.
Each node in a Binary Tree has three parts:
Data
Pointer to the left child
Pointer to the right child
Properties of Binary Tree
The maximum number of nodes at level L of a binary tree is 2L.
The maximum number of nodes in a binary tree of height H is 2H+1 – 1.
Total number of leaf nodes in a binary tree = total number of nodes with 2 children + 1.
Lets dive into code:
class TreeNode {
int data;
TreeNode left, right;
public TreeNode(int data) {
this.data = data;
left = right = null;
}
}
/**
* Depth-first search is a type of traversal that goes deep as much as possible in every child
* before exploring the next sibling.
*
* <p>There are several ways to perform a depth-first search: in-order, pre-order and post-order.
*/
/**
* The in-order traversal consists of first visiting the left sub-tree, then the root node, and finally the right sub-tree:
*/
public void traverseInOrder(TreeNode node) {
if (node == null) return;
traverseInOrder(node.left);
System.out.print(" " + node.data);
traverseInOrder(node.right);
}
/**
* Pre-order traversal visits first the root node, then the left sub-tree and finally the right sub-tree.
*/
public void traversePreOrder(TreeNode node) {
if (node == null) return;
System.out.print(" " + node.data);
traversePreOrder(node.left);
traversePreOrder(node.right);
}
/**
* Post.order traversal visits the left sub-tree, the right sub-tree and the root node at the end.
*/
public void traversePostOrder(TreeNode node) {
if (node == null) return;
traversePostOrder(node.left);
traversePostOrder(node.right);
System.out.print(" " + node.data);
}
/**
* Breadth-First Search - This is another common type of traversal that visits all the nodes of a
* level before going to the next level.
*
* <p>This kind of traversal is also called level-order, and visits all the levels of the tree
* starting from the root, and from left to right.
*
* <p>For the implementation, we’ll use a Queue to hold the nodes from each level in order. We’ll extract each node from the list, print its values, then add its children to the queue:
*/
public void traverseLevelOrder(TreeNode node) {
Queue<TreeNode> nodes = new LinkedList<>();
nodes.add(node);
while (!nodes.isEmpty()) {
TreeNode n = nodes.remove();
if (n == null) {
continue;
}
System.out.print(" " + n.data);
nodes.add(n.left);
nodes.add(n.right);
}
}